Introduction: The Growing Need for E-Waste Shredding Solutions
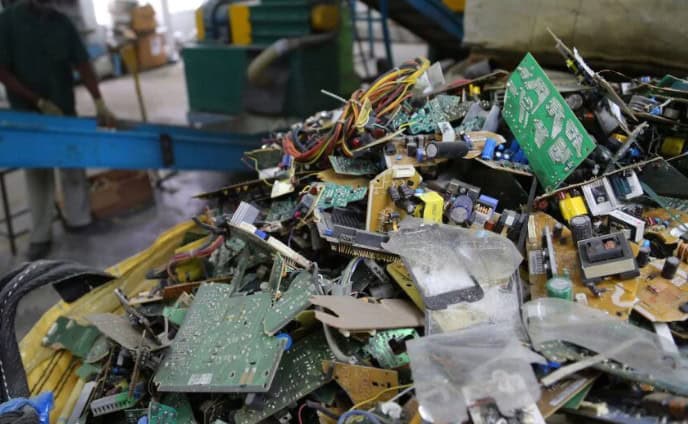
With over 57 million tons of electronic waste generated globally each year (Global E-Waste Monitor 2023), the need for efficient recycling solutions has never been greater. Among the most effective machines for processing electronic components is the single shaft shredder—a powerful, versatile tool designed to break down circuit boards, wires, and other e-waste into recyclable materials.

This comprehensive guide will explore:
✅ What a single shaft shredder is and how it works
✅ Why it’s ideal for shredding electronic components
✅ The shredding process and efficiency rates
✅ How shredded e-waste is repurposed
✅ Key factors in choosing the right shredder
Whether you’re an e-waste recycler, manufacturer, or sustainability-focused business, this guide will help you understand how single shaft shredders maximize electronic waste recovery.
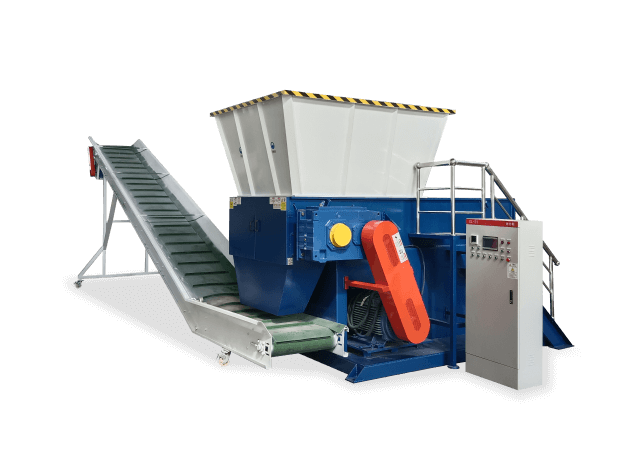
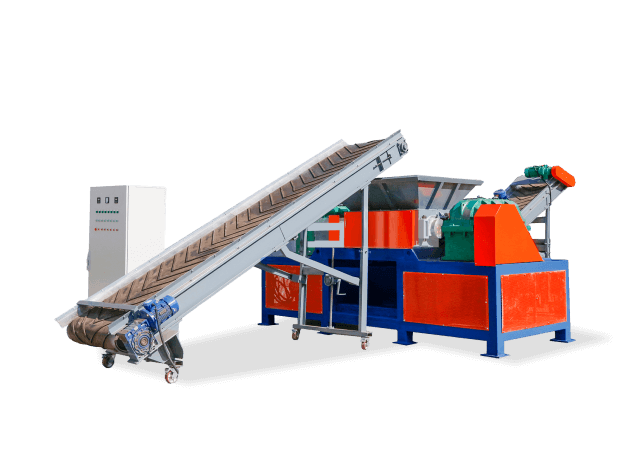
1. What Is a Single Shaft Shredder?
A single shaft shredder is a heavy-duty industrial machine designed to reduce materials into smaller, uniform pieces through cutting, tearing, and shearing. Unlike dual-shaft models, it uses one rotating shaft with hardened steel blades to process materials efficiently.
Key Components:
– Rotating Shaft – The core mechanism with welded or bolted blades
– Hopper – Where electronic waste is fed into the machine
– Screen/Grate – Controls output size (typically 10-50mm)
– Drive System – Electric or hydraulic motor for power
– Control Panel – Adjusts speed and monitors performance
How It Works:
1. Feeding – Electronic components enter through the hopper
2. Shredding – Blades cut, tear, and crush materials
3. Screening – Particles pass through a mesh for uniform sizing
4. Discharge – Shredded material is collected for recycling
Single shaft shredders excel at processing mixed electronic waste, including brittle PCBs, plastic casings, and metal components.
2. Key Applications of Single Shaft Shredders in Electronics Recycling
Single shaft shredders are widely used for:
✔ Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs)
– Recovers copper, gold, and silver from shredded fragments
– Reduces hazardous material leakage (lead, mercury)
✔ Wires & Cables
– Separates copper/aluminum conductors from insulation
– Enables efficient metal recovery
✔ Plastic Housings
– Shreds casings from computers, TVs, and appliances
– Prepares plastic for pelletizing and reuse
✔ Batteries (Li-ion, Ni-Cd)
– Safely breaks down battery cells for material extraction
– Prevents toxic chemical leaks
✔ Data-Bearing Devices (Hard Drives, SSDs)
– Ensures complete data destruction for security compliance (GDPR, HIPAA)
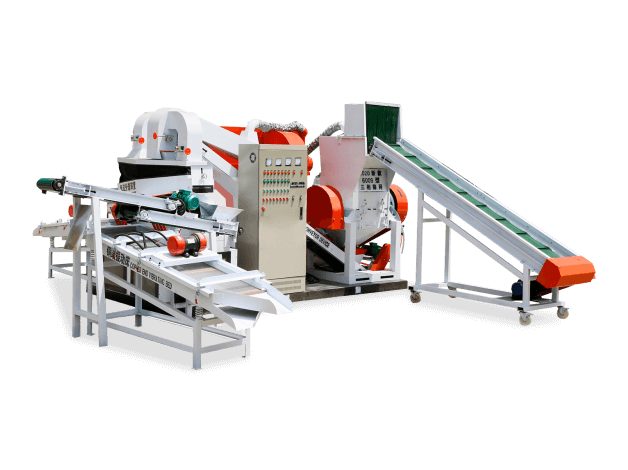
3. Shredding Efficiency: How Single Shaft Shredders Process Electronic Components
Shred video display:
3.1 Shredding Process Breakdown
1. Pre-Shredding – Bulky items are reduced to manageable sizes
2. Primary Shredding – Blades cut materials into smaller chunks
3. Fine Shredding – Particles pass through a screen for uniform output
4. Separation – Metals, plastics, and glass are sorted for recycling
3.2 Efficiency Factors
– Blade Design – Hardened steel or tungsten carbide for durability
– Motor Power – 30-200 HP for different throughput needs
– Output Size – Adjustable screens (10mm-50mm) for optimal recovery
– Throughput Capacity – Processes 500-5,000 kg/hour, depending on model
3.3 Advantages Over Other Shredders
| Feature | Single Shaft Shredder | Dual-Shaft Shredder |
| Energy Use | Lower power consumption | Higher energy demand |
| Maintenance | Easier blade replacement | More complex upkeep |
| Output Control | Adjustable screen size | Fixed blade gap |
| Best For | Mixed e-waste, PCBs, wires | Heavy-duty metal scrap |
4. What Happens to Shredded Electronic Components?
4.1 Metal Recovery
– Copper, gold, silver extracted from PCBs via smelting
– Aluminum recovered from casings and heat sinks
4.2 Plastic Recycling
– ABS, PVC, and polycarbonate shredded plastic is pelletized for reuse
4.3 Glass & Ceramic Reuse
– CRT glass from monitors repurposed for construction materials
4.4 Hazardous Material Neutralization
– Lead, mercury, and cadmium safely disposed of per EPA/WEEE regulations
4.5 Data Security Compliance
– Shredded hard drives ensure irrecoverable data destruction
5. How to Choose the Right Single Shaft Shredder for Electronic Waste
5.1 Material Type Considerations
– Soft plastics & thin metals → Standard steel blades
– Hard PCBs & thick wires → Tungsten carbide blades
5.2 Required Output Size
– Coarse shredding (30-50mm) – For initial size reduction
– Fine shredding (5-20mm) – Better for metal recovery
5.3 Motor Power & Throughput
– Small operations → 20-50 HP (300-1,000 kg/hour)
– Large facilities → 100-200 HP (3,000-5,000 kg/hour)
5.4 Safety & Maintenance Features
– Overload protection prevents motor burnout
– Automatic lubrication extends blade life
– Dust extraction systems reduce airborne contaminants
5.5 Budget & ROI Analysis
– Entry-level models → $20,000-$50,000
– Industrial-grade shredders → $80,000-$200,000+
Conclusion: Why Single Shaft Shredders Are the Future of E-Waste Recycling
Single shaft shredders offer:
✔ Higher efficiency in processing mixed e-waste
✔ Lower operational costs than dual-shaft alternatives
✔ Better material recovery rates for metals & plastics
✔ Compliance with global e-waste regulations
For businesses handling electronic waste, investing in the right shredder improves sustainability, profitability, and regulatory compliance.
Need expert advice on selecting a shredder? Contact us for a free consultation!