In today’s information-driven world, paper waste management has evolved from simple disposal to a complex security and environmental imperative. Businesses generate mountains of confidential documents, financial records, and proprietary information on paper that cannot simply be thrown away. At the heart of modern secure destruction systems stands the dual-shaft shredder, a technological powerhouse specifically engineered to transform sensitive paper waste into unreconstructable material. This comprehensive guide explores why dual-shaft shredding represents the gold standard in paper waste processing, examining its mechanics, advantages, applications, and operational best practices.
Chapter 1: Understanding Dual-Shaft Shredder Technology
1.1 Core Design and Mechanics
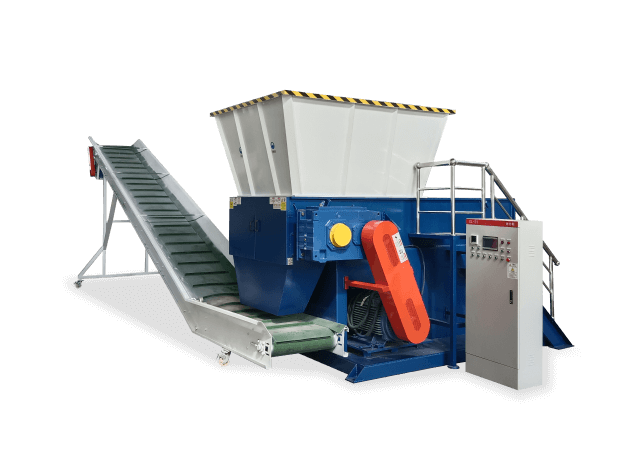
Unlike conventional single-shaft shredders that use a rotary mechanism against a stationary edge, dual-shaft shredders employ two parallel, intermeshing shafts equipped with cutting discs or blades. Each shaft rotates at a carefully synchronized speed, typically between 20-60 RPM, creating a powerful shearing and tearing action.
The cutting discs are strategically staggered between the shafts so that each disc on one shaft rotates between two discs on the opposite shaft. This configuration creates a scissor-like cutting motion that grabs, pulls, and reduces material with exceptional efficiency. The shafts are typically driven by high-torque hydraulic or electric motors through a heavy-duty gearbox, providing the immense power needed to process large volumes continuously.
1.2 Key Components Breakdown
Cutting Shafts and Discs: Made from hardened alloy steel (often 40CrNiMoA or similar), heat-treated to 48-52 HRC for exceptional wear resistance. The discs feature multiple cutting edges to extend service life.
- Drive System: Consists of high-efficiency electric motors (typically 30-200 HP depending on size) coupled with planetary gear reducers that provide the necessary torque while maintaining energy efficiency.
- Hydraulic System: Powers the pushing ram that feeds material into the cutting zone, controls shaft speed and direction, and facilitates maintenance functions like opening the cutting chamber.
- Control Panel: Modern units feature PLC-based controls with touchscreen interfaces, allowing operators to adjust parameters, monitor performance, and diagnose issues. Many include automatic reverse functions to clear jams and reduce downtime.
- Frame and Construction: Built from heavy-duty steel plate (minimum 20mm at stress points) with reinforced welding at all critical joints to withstand constant high-stress operation.
1.3 Material Reduction Process
The shredding action occurs in three distinct phases:
1. Initial Engagement: The rotating shafts grab and pull paper into the cutting zone through positive feed action, eliminating the need for manual pushing in most configurations.
2. Shearing Phase: As material enters between the intermeshing cutting discs, it experiences powerful shearing forces that initiate the size reduction process.
3. Size Refinement: Material continues through multiple cutting zones along the shaft length, with each pass creating progressively smaller fragments until particles exit through an adjustable screen at the bottom.
Chapter 2: Why Dual-Shaft Technology Excels for Paper Waste
2.1 Unmatched Security Level
For paper containing sensitive information, dual-shaft shredders provide P-5 security level destruction according to DIN 66399 standards (the international standard for shredder security). They produce output particles typically measuring 2-10mm in cross-section—small enough to meet even stringent government and military requirements for document destruction. Unlike strip-cut shredders that create readable ribbons, dual-shaft output is completely unreconstructable, providing absolute security against information reconstruction attempts.
2.2 Superior Volume Processing
While office shredders might process 10-30 sheets per pass, industrial dual-shaft systems can handle 500-5,000 kg of paper per hour depending on model size. Their continuous feed capability—often with conveyorized infeed systems—allows for non-stop operation. This high-volume capacity makes them ideal for centralized destruction facilities, large corporations, and document destruction services.
2.3 Exceptional Durability and Reliability
The robust construction of dual-shaft shredders translates to significantly longer operational lifespans compared to alternative technologies. With proper maintenance, these machines can operate for 15,000-20,000 hours before requiring major overhaul. Their ability to handle contaminants (like staples, paper clips, and folder fasteners) without damage reduces downtime and maintenance costs compared to more delicate shredding technologies.
2.4 Energy Efficiency Considerations
Modern dual-shaft shredders incorporate several energy-saving features:
Variable frequency drives (VFDs) that adjust motor speed based on load requirements
Hydraulic systems with load-sensing technology that minimize energy consumption during idle periods
High-efficiency IE3 or IE4 class motors that convert more electrical input to mechanical output
Automatic standby modes that activate during extended feeding pauses
These features can reduce energy consumption by 25-40% compared to older constant-speed models while maintaining peak performance during actual shredding operations.
Chapter 3: Industrial Applications and Configurations
3.1 Commercial and Industrial Settings
Document Destruction Services: Mobile and stationary systems for confidential document destruction with audit trail capabilities
Financial Institutions: Banks, insurance companies, and accounting firms processing sensitive client documents
Government and Military Facilities: Meeting strict security protocols for classified material destruction
Manufacturing Facilities: Destroying product specifications, quality documents, and proprietary research
Healthcare Organizations: Compliant destruction of patient records under HIPAA and similar regulations
3.2 Specialized System Configurations
- Stand-Alone Shredders: Basic units for operations with pre-sorted paper streams
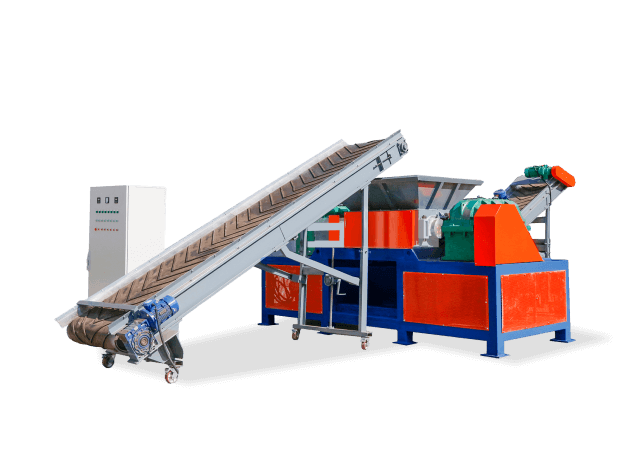
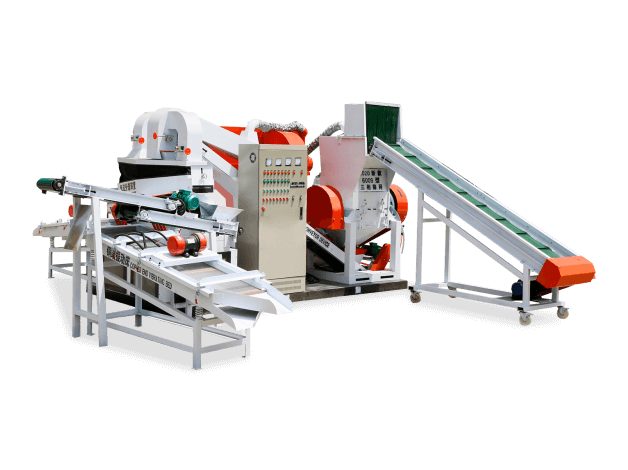
- Integrated Shredding Systems: Combined with conveyors, balers, and air filtration systems for complete material handling
- Mobile Shredding Units: Truck-mounted systems for on-site destruction services
- High-Security Shredding Lines: Multiple shredding stages followed by briquetting for maximum security applications
3.3 Output Handling and Material Recovery
The shredded paper from dual-shaft systems presents valuable recovery opportunities:
Baling: Shredded paper can be compacted into dense bales (typically 400-600 kg/m³) for efficient transportation
Pulping Preparation: Uniformly shredded paper is ideal for recycling facilities as it requires less preprocessing
Alternative Fuel Production: High-calorific value material for waste-to-energy facilities (approximately 15-17 MJ/kg)
Composting Material: Carbon-rich component for industrial composting operations when free of contaminants
Safety Considerations
- Lockout/Tagout Procedures: Strict adherence to LOTO protocols during maintenance
- Safety Interlocks: Regular testing of all safety switches and door interlocks
- Emergency Stop Systems: Functionality testing of all emergency stop buttons and pull cords
- Dust Control: Implementation of proper dust collection to prevent respiratory hazards and explosion risks (paper dust can be explosive at concentrations above 60g/m³)
- Operator Training: Comprehensive training on proper operation, jam clearing procedures, and emergency response
Conclusion: The Strategic Value of Dual-Shaft Shredding
Dual-shaft shredding technology represents more than just equipment—it embodies a comprehensive approach to paper waste management that addresses security, efficiency, and sustainability in equal measure. As data security concerns intensify and environmental regulations tighten, this technology provides a robust solution that scales from corporate offices to industrial recycling facilities.
The versatility and durability of dual-shaft systems ensure they adapt to changing material streams and security requirements, protecting both information and the bottom line. For organizations serious about responsible information lifecycle management, dual-shaft paper shredding isn’t merely an option—it’s an essential component of modern operational infrastructure.
Organizations implementing these systems should partner with reputable manufacturers that offer comprehensive technical support, operator training, and maintenance programs to maximize system lifespan and return on investment. With proper implementation and operation, dual-shaft shredding technology delivers security, efficiency, and environmental benefits that justify its position as the industrial standard for paper waste destruction.